Assume 3 examples to explain the classes of IP address, how we can calculate the total network and hosts IDs in each class using shortest methods do all the necessary steps and use concepts to explain the worth of each class.
IP
address:
IP addresses are
unique numeric code that assign to your each device in your network, it can be
public or private, because not every computer or device assign public ip
address, the main key difference is that public ip is the main address which
you buy from any API like zong 4G etc.
The are two
types of ip addresses
Ipv4 ipv6
Ipv4 is 32 bit
having 4 octets in each address and Ip 6 having 132 bit and having 8 octets.
Due to excessive
use of internet and most of the devices gone to the internet that’s why the Ipv
6 introduced
Example of ip
address:
As we having a
phone number which is unique number for each other in the same way every device
in a network have unique ip address for communication. Like every number have
area code and id, in the same way every ip contains network id and the number
of host id.
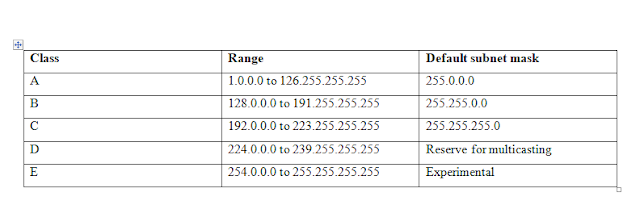
There are 5 main
classes of ip classes A to C allocated ip address for enterprise home etc,
class D for multicasting and class E reserve for future. The main purpose of
division of ip in different classes to identify the main claims in future. Like
if there is any issue cyber issues or any crime occur it should be easily
determine that this ip belongs to which class and then the targeted area for
investigation will be shortest.
Class “A”
calculation with the help of example:
For example we creating local network with the range of 1st
class.
This class start from 0 to 127 so there is number of host
are as follows:
The representation of class “A” N.H.H.H
which means there is 1 octet for netwrok id and other 3
determines the host id.
How we calculate the network id of class “A”:
Class A:
00000000.H.H.H
We fix 1s bit as “0” which never be change because if its
change it will may lie on other class range. So when we fix
1st bit it will be determines the range of class A
other will be change
Like
|
0 |
7bit HOST |
24 bit HOST |
For network id calculation:
2^7-2 = 126 network ID
For HOST id
calculation:
There is 3 octet which determines the host id and one octet
equals 8 bit and 3 octet will be equals to 24 bit so the according to the
formula of calculation host id in 1st class will be
2^24-2 = 17,777,214 host
id
Class “B”
calculation with the help of example:
Class “B” starts from 128 and end 191 so the range of host
and network id is always fix.
The representation of class “A” N.N.H.H
How we calculate the network id of class “B”:
Class B:
10000000.H.H.H
Which means there is 2 octet of network id and 2 octet of
host id.
In the same way we calculate class “A” we calculate the class
“ B netwrok and host id in class “B” we
fix 1st 2 bit which is “10” and other will be change so this way
class “B” always lie in the class “B” address range.
Like
|
10 |
14 bit HOST |
16 bit HOST |
For network id
calculation:
1st 2 octet of network id and for calculation we
fix the 1st 2 bit of 1st octet as “10” which is shown
above, so according to formula:
2^14-2 = 16384 network
ID
For HOST id calculation:
There is 2 octet which determines the host id and one octet
equals 8 bit and 2 octet will be equals to 16 bit so the according to the
formula of calculation host id in 1st class will be
2^14-2 = 65534 host id
Class “C”
calculation with the help of example:
In this class “C” there is 3 octets of network id and 1 octet
reserve for host id
The representation of class “C” N.N.N.H
How we calculate the network id of class “C”:
Class C: 11000000.H.H.H
Which means 1st 3 octets represents network id and
last represent host id. For calculation of the we fix 1st 3 bits of
the network id so 1st 3 bit not change other will be change that’s
why it will not lie in other class range.
Like
|
110 |
14 bit HOST |
16 bit HOST |
For network id
calculation:
1st 2 octet of network id and for calculation we
fix the 1st 2 bit of 1st octet as “10” which is shown
above, so according to formula:
2^21-2 = 2097152 network
ID
Class “C”
calculation with the help of example:
In this class “C” there is 3 octets of network id and 1 octet
reserve for host id
The representation of class “C” N.N.N.H
How we calculate the network id of class “C”:
Class C: 11000000.H.H.H
Which means 1st 3 octets represents network id and
last represent host id. For calculation of the we fix 1st 3 bits of
the network id so 1st 3 bit not change other will be change that’s
why it will not lie in other class range.
Like
|
110 |
14 bit HOST |
16 bit HOST |
For network id
calculation:
1st 2 octet of network id and for calculation we
fix the 1st 2 bit of 1st octet as “10” which is shown
above, so according to formula:
2^21-2 = 2097152 network
ID
For HOST id
calculation:
There is 1 octet which determines the host id and one octet
equals 8 bit so the according to the formula of calculation host id in 1st
class will be
2^8-2 = 254 host id








0 comments:
Post a Comment